Sullivan is recognized by Guinness World Records as the person struck by lightning more recorded times than any other human being.
Sullivan survived but end up Tragedy the seven strikes and was referred to as a "human lightning conductor.
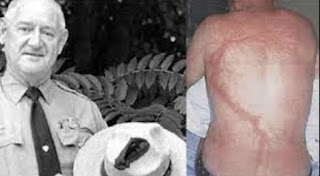
Roy Cleveland Sullivan (February 7, 1912 – September 28, 1983) was an American park ranger in Shenandoah National Park in Virginia. Between 1942 and 1977, Sullivan was claimed to have been struck by lightning on seven occasions, surviving all of them. For this reason, he gained the nicknames "Human Lightning Conductor" and "Human Lightning Rod". Sullivan is recognized by Guinness World Records as the person struck by lightning more recorded times than any other human being
Roy was born in Greene County, Virginia, on February 7, 1912. He started working as a ranger in Shenandoah National Park in 1936. Sullivan was described as a brawny man with a broad, rugged face, who resembled the actor Gene Hackman. He was said to have been avoided by people during the later years of his life, owing to fears of being struck by lightning, and that saddened him. He once recalled: "For instance, I was walking with the Chief Ranger one day when lightning struck way off” (in the distance). The Chief said, "I'll see you later".
On the morning of September 28, 1983, Sullivan died at the age of 71 from a self-inflicted gunshot wound to the head. Two of his ranger hats are on display at two Guinness World Exhibit Halls in New York City and South Carolina.
Common injuries caused by lightning include: muscle pains, broken bones, cardiac arrest, confusion, hearing loss, seizures, burns, behavioral changes, and ocular cataracts. Loss of consciousness is very common immediately after a strike.
Lightning burns result from energy caused by lightning strikes, and are characterized by a unique pattern of skin lesions. These tree-like lesions resemble feathering or ferning, and are also called Lichtenberg figures. The marks are formed when capillaries beneath the skin rupture due to the electrical discharge and they usually appear "within hours" of the strike though they tend to disappear within a few days. They also generally occur on the upper body. The brief duration of the exposure frequently limits the damage to the outer layer of skin.
The intense heat generated by a lightning strike can burn tissue, and cause lung damage, and the chest can be damaged by the mechanical force of rapidly expanding heated air.
Just as heat can cause expanding air in the lungs, the explosive shock wave created by lightning (the cause of thunder) can cause concussive and hearing damage at extremely close range. Other physical injury can be caused by objects damaged or thrown by the lightning strike. For example, lightning striking a nearby tree may vaporize sap, and the steam explosion often causes bark and wood fragments to be explosively ejected.
Lightning strikes can also induce a transient paralysis known as 'keraunoparalysis'. Signs and symptoms of keraunoparalysis include lack of pulse, pallor or cyanosis, and motor and sensory loss in the extremities. However, keraunoparalysis usually resolves within a few hours.
Thanks for reading leave your thoughts in the comments section below
Read more on our Rare History Channel



Comments
Post a Comment